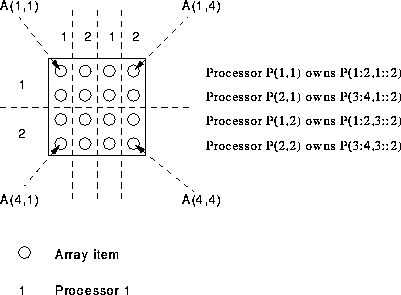
Figure 20: Visualisation of 2D Distribution
2D distribution is simple. The example has BLOCK distribution in the first dimension (traversing the rows) and CYCLIC in the second dimension (traversing the columns).
PROGRAM Skwiffy
IMPLICIT NONE
REAL, DIMENSION(4,4) :: A, B, C
!HPF$ PROCESSORS, DIMENSION(2,2) :: P
!HPF$ DISTRIBUTE (BLOCK,CYCLIC) ONTO P :: A, B, C
B = 1; C = 1; A = B + C
END PROGRAM Skwiffy
Thusly, the first dimension is partitioned into equal sized blocks and the second dimension is divided up in a round robin fashion. It transpires that (see Figure 20:

Figure 20: Visualisation of 2D Distribution